Outline
Note
Zenswap is currently under active development. Features, functionality, and documentation are subject to change as we refine and improve things. While we strive to maintain consistency, there may be updates or adjustments in the future. We recommend checking back regularly for the latest information and updates. Thank you for your understanding and support!
Overview
Zenswap is a cross-chain swap solution that enables seamless native asset exchanges across different blockchains and networks. By leveraging USDC routing, Zenswap provides users boundless liquidity and eliminates the complexity of cross-chain interactions. It is powered by Analog GMP and Circle CCTP, ensuring secure and efficient transactions. Currently, Zenswap sources liquidity from major DEXs, such as Uniswap, and supports developers in integrating its functionality into custom smart contracts. Future iterations aim to be DEX-agnostic, supporting native token swaps across multiple chains.
Features
Capital efficiency: Addresses liquidity fragmentation by pairing all assets with USDC, minimizing slippage, and attracting competitive market makers. For more details, see “Liquidity Management”.
Boosted liquidity/Boost Mode: Zenswap’s novel Boost Mode, developed by Analog, enables cross-chain swaps to be settled in near-instant time, significantly enhancing efficiency and UX. Check out “Boost Mode” for more info.
Composability: Zenswap is a fully composable solution, meaning you can append extra logic to the asset transfer logic on the target blockchain. Imagine unstaking on chain A and then transferring the unstaked asset to chain B to use as collateral for a loan. Check out “SDK Quickstart” & “API Quickstart” to get started.
Optimized route selection: Algorithm evaluates routes based on fees, speed, and liquidity, including Boost Mode availability. For more details, see “Route Selection”.
Real-time transaction transparency: Users track swap progress through detailed status updates (e.g., SourceSwap, USDCburn, Completed). See “Transaction Status Tracking”.
Supported Blockchains & Assets
Blockchains
| Version | Networks |
|---|---|
| Testnet: Classic Mode | Ethereum Sepolia |
| Base Sepolia | |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | |
| Mainnet: Boost Mode | Arbitrum |
| Avalanche | |
| Base | |
| Ethereum |
Assets
Using USDC pairs, Zenswap leverages DEXs like Uniswap for native swaps across supported blockchains, initially supporting Uniswap's token list, found here.
Getting Started
Zenswap offers three primary tools for cross-chain swaps:
- Zenswap App: A user-friendly dApp for seamless cross-chain swaps. The testnet version is live at https://testnet.zenswap.io/#/swap
- Zenswap SDK: A developer toolkit to integrate cross-chain swaps into custom dApps. For more details, see SDK Quickstart.
- Zenswap API: Enables programmatic access to Zenswap’s routing, liquidity, and swap execution. For more details, see API Quickstart.
Quickstart Guide
For Developers
Zenswap offers a fully customizable SDK integration to enable cross-chain activities within your dApps.
SDK Quickstart
Prerequisites:
- Node.js v18+
- Wallet with testnet funds.
Steps:
- Installation/setup: To integrate the Zenswap SDK into your project, use your preferred package manager:
npm install @zenswap-analog/sdk # or yarn add @zenswap-analog/sdk # or pnpm add @zenswap-analog/sdk - Initialize SwapRouterSwapRouter is the main entry point for Zenswap smart contract interactions.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkId, ChainId, getNetworkId, getChainId, } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk"; // Create router instance with default configurations const router = new SwapRouter(); // Or override specific configurations const customContracts = { [ChainId.EthereumMainnet]: { zenswap: "0x...", // Your deployed Zenswap contract address gmpPlugin: "0x...", // Your deployed GMP plugin address gmpGateway: "0x...", // Your deployed GMP gateway address }, }; const customGmpIds = { [ChainId.EthereumMainnet]: 1, }; const customFeePercent = 0.3; // 0.3% const customFeeRecipient = "0x..."; // Create router instance with custom configurations const customRouter = new SwapRouter( customContracts, // null to use defaults customGmpIds, // null to use defaults customFeePercent, // null to use defaults customFeeRecipient // null to use defaults ); - Find a Swap Route Find the best path to swap tokens between different chains, optimizing for cost, efficiency, and minimal price slippage.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk"; // Define input parameters const swapParams = { input: tokenIn, // NetworkToken object for input token output: tokenOut, // NetworkToken object for output token amount: "1.5", // Amount to swap as string recipient: "0x...", // Recipient address slippagePercent: 0.5, // Slippage tolerance (0.5%) deadlineInSeconds: 1800, // Transaction deadline (30 minutes) }; // Find the best route const route = await router.findRoute(swapParams); if (route) { console.log("Swap route found:"); console.log("Input amount:", route.input.amount); console.log("Output amount:", route.output.amount); console.log("Price impact:", route.priceImpact, "%"); console.log("Strategy:", route.strategy); // The route.method contains the transaction parameters const txParams = route.method?.parameters; // Execute the transaction using your preferred web3 provider // e.g., with ethers.js: // const tx = await signer.sendTransaction(txParams); } - Cross-Chain Transfer Example Example of a cross-chain transfer from Ethereum to Polygon.
const transferParams = { input: usdcEthereum, // USDC on Ethereum output: usdcPolygon, // USDC on Polygon amount: "100", // Amount to transfer recipient: "0x...", // Recipient address slippagePercent: 0.1, deadlineInSeconds: 1800, }; const transferRoute = await router.findRoute(transferParams); // The transferRoute.method contains the transaction parameters // The transferRoute.fee contains the estimated gas fee // The transferRoute.transferFee contains the cross-chain transfer fee
API Quickstart
Endpoint: POST /api/v1/swap
Request:
// Request Body placeholder
{
"sourceChainId": "",
"destinationChainId": "",
"sourceTokenAddress": "",
"destinationTokenAddress": "",
"amount": "",
"recipientAddress": "",
"slippageTolerance": 0.005, // Example: 0.5%
"useTurbo": false // Optional: set to true to try Boost Mode
}
Response:
// Response Body placeholder
{
"transactionId": "",
"status": "Initial",
"estimatedCompletionTime": ""
// ... other relevant details
}
For Users
- Visit Zenswap Testnet.
- Connect your wallet (e.g., MetaMask).
- Select source/destination chains and tokens.
- Review swap details (fees, slippage, estimated time).
- Confirm and execute the swap.
Using Boost Mode:
- Select “Boost Mode” during route selection if liquidity is sufficient on the destination chain.
- Confirm transaction for high-speed execution.
Using Zenswap
Connecting Your Wallet
- Launch the Zenswap Testnet.
- Click “Connect wallet”
- Select your preferred wallet provider and follow the prompts.
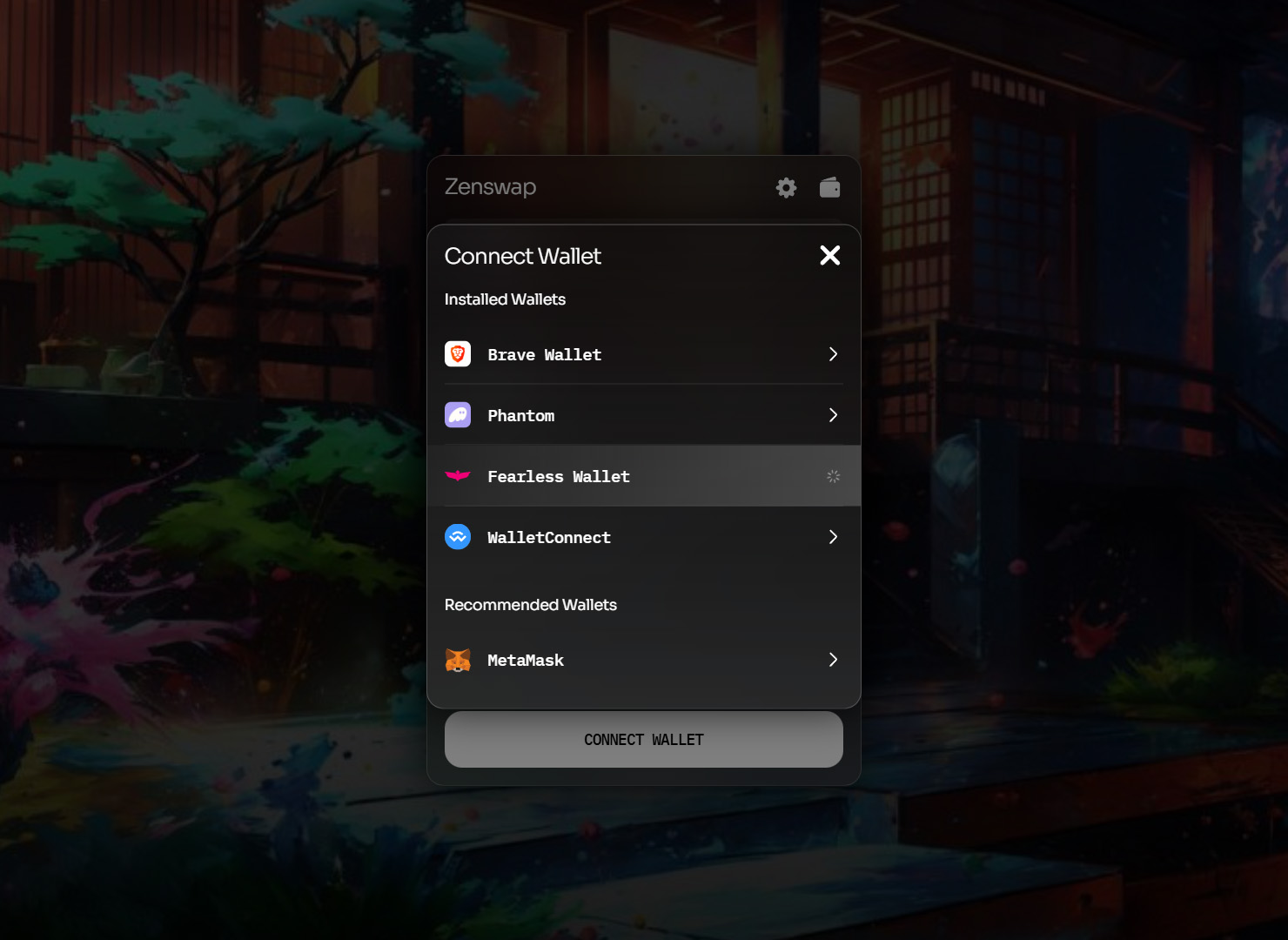
Swapping via Zenswap App
- Connect Wallet:
- Click “Connect Wallet” and authorize.
- Select Chains/Tokens:
- Choose source/destination chains (e.g., Ethereum → Polygon or Ethereum → Arbitrum).
- Select tokens (e.g., ETH → MATIC or ETH → ARB).
- Review Details:
- Before confirming a swap, review these important details by clicking on the Settings button:
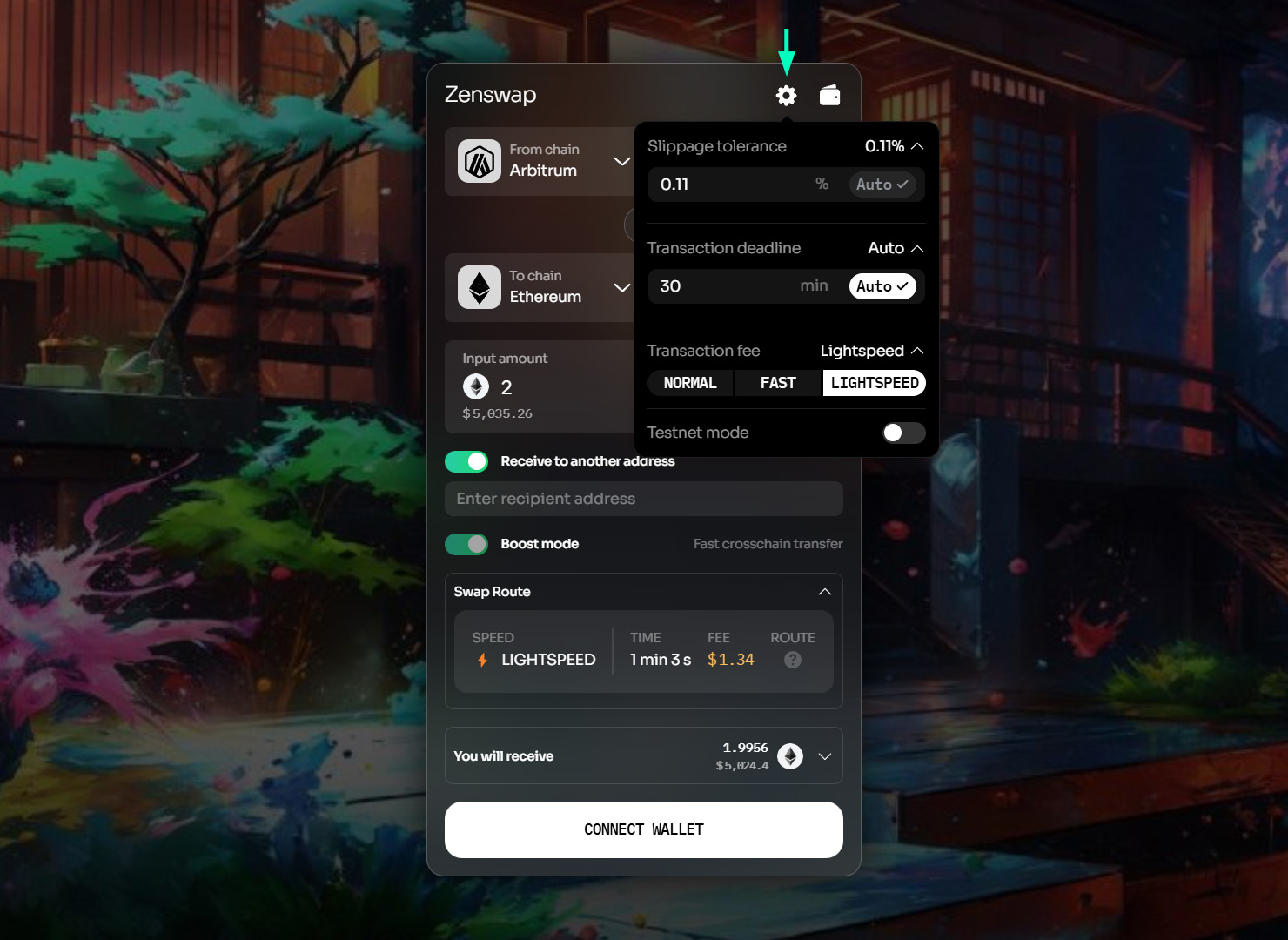
- Check slippage tolerance, transaction deadline, and transaction fee.
- Slippage tolerance: Maximum acceptable price change
- Transaction deadline: Expected completion time
- Transaction fee: Fee deducted for cross-chain transaction
- Enter the recipient’s address (if it’s different from the sender’s address).
- Enable Boost Mode (if available and desired).
- Select the route for your swap transaction (see Route Selection).
- Check slippage tolerance, transaction deadline, and transaction fee.
- Before confirming a swap, review these important details by clicking on the Settings button:
- Execute Swap:
- Confirm the transaction in your wallet.
Route Selection
- When you select tokens and chains, Zenswap calculates optimal routes for your swap. Each route option displays:
- Approximate time: Expected completion time.
- Approximate fees: Fee deducted for the cross-chain transaction.
- Chain path details: Details about the chains involved.
- If available, Boost Mode will appear as an additional option.
- Select your preferred route option and click “Swap.”
Swapping Basics
Overview
Zenswap offers seamless cross-chain swaps using Analog GMP and Circle CCTP. Users deposit tokens on the origin chain, and the protocol handles the rest, automatically swapping assets on the destination chain without further user input. The swapping process starts when users deposit their tokens on the origin blockchain. The protocol uses Analog GMP and Circle CCTP to make cross-chain swaps more secure and efficient.
Whenever funds are deposited on the origin chain, Analog GMP and Circle CCTP witness the deposit event and subsequently relay the information to the destination chain, where the tokens are swapped to the corresponding assets.
Key Concepts
Native Cross-Chain Swap
Refers to exchanging one native token (e.g., ETH on Ethereum) for another token (e.g., BNB on BNB Chain).
Note
Note that the exchanging native tokens reside on different blockchains.
Zenswap leverages USDC as a routing layer to facilitate swaps across supported blockchains. For example, if Alice wants to swap native ETH on the Ethereum for BNB on the BNB Chain, here’s how the Zenswap protocol will enable the swap (using the classic service):
Example 1 (Classic Service): MATIC to BNB Swap
- Your token (MATIC) on the source chain (Polygon) is swapped to USDC.
- The USDC is burned via Circle CCTP on Polygon.
- The burn parameters are transferred to the destination chain (BNB Chain) via Analog GMP.
- USDC is minted on the BNB Chain.
- The USDC is swapped to your desired token (BNB).
- BNB is sent to your wallet on the BNB Chain.
Example 2: ETH to ARB Swap with Boost Mode
Bob wants to quickly swap ETH on Ethereum for ARB on Arbitrum with Boost Mode enabled:
- Bob deposits ETH into Zenswap's contracts on Ethereum.
- The protocol swaps ETH to USDC on Ethereum.
- With Boost Mode, an LP instantly provides USDC on Arbitrum.
- The USDC is immediately swapped to ARB on Arbitrum.
- Bob receives ARB in his wallet almost instantly.
In the background, the normal Analog GMP and CCTP process completes and replenishes the LP’s funds.
Liquidity Management
The defining idea of Zenswap is boundless liquidity: liquidity that allows users to swap any amount of USDC without experiencing slippages. Unlike other protocols constrained by limited liquidity pools, Zenswap, supported by Circle CCTP, utilizes a common base pair for all pools. This novel approach minimizes liquidity fragmentation and significantly reduces overall slippages.
Transaction Finality
Transaction finality denotes the irreversible point at which a transaction is deemed final on the blockchain. The degree of finality varies across blockchains, with some offering instant finality while others require multiple confirmations.
This disparity in finality can cause delays during cross-chain swaps, particularly for blockchains like Ethereum, often resulting in substantial waiting periods. For Zenswap, the duration of the swap largely depends on the finality time of the origin chain for classic (i.e., non-Boost Mode) transactions.
Analog GMP and Circle CCTP prioritize security by delaying the minting process on the destination chain until the burning process on the source chain is definitively confirmed, thus mitigating the risk of chain reorgs.
Boost Mode
Boost Mode enables seamless cross-chain USDC transfers via Circle's CCTP v2 protocol with added reliability features. Here is how it works:
- Initiation
- User calls
submit()on ZenSwapCCTPv2 with:pluginParams: Destination plugin, recipient, fallback address, max fee, and reward.extraData: Swap instructions for the destination chain.amount: USDC to bridge.
- Protocol deducts a fee (basis points) from the
amount.
- User calls
- Cross-Chain Execution
- USDC burned on the source chain via Circle’s CCTP.
PluginMessageSentevent emitted, triggering attestation.
- Attestation & Relaying
- Relayers monitor Circle’s API for attestations.
- Attestation + message relayed to the destination chain.
- Destination Handling
receiveMessage()on the destination chain:- Mints USDC.
- Pays relayer reward.
- Executes
onReceive()on ZenSwap for the swap:- Success: Tokens sent to the recipient.
- Failure: USDC sent to fallback address.
How Swapping Works
A general description of the swap process can be described as follows:
Step 1: Initiation of the swap
You can accomplish this step via three methods:
- Zenswap App.
- Zenswap SDK. See SDK Quickstart for more details.
- Zenswap API. See API Quickstart for more details.
Step 2: Attestation of the deposit event
Analog GMP and Circle CCTP monitor the deposit event on the source chain’s relevant gateways. Upon witnessing a deposit for a swap, the transaction is registered on the Timechain and Circle’s Attestation Service.
Note that a delay exists between the initial deposit and its subsequent confirmation on these services. For further information, refer to the section on “Transaction Finality”.
Step 3: Processing the swap
Once the swap is witnessed and validated, it is ready to be executed by the Zenswap protocol. For more details, check out “Architectural Components” and “Transaction Lifecycle”.
Technology & Architecture
Tech Stack
The Zenswap tech stack can be broken down into three core components:
- Zenswap Contracts: Facilitates token swaps on the supported DEX, with optional cross-chain functionality via plugins. It supports:
- Local Swaps: Swap tokens on the current chain and send to a recipient.
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Swap tokens, bridge them via a plugin, and execute another swap on the destination chain.
- Circle CCTP: Burns/mints USDC across chains securely.
- Workflow: Burn → Attest → Mint.
- A user burns USDC on the source chain.
- Circle Attestation Service observes and attests to the burn event.
- Any user or third party relays the message and attestation to the target blockchain.
- A user receives minted USDC on the target chain.
- Workflow: Burn → Attest → Mint.
- Analog GMP: Facilitates cross-chain messaging via Timechain.
- Workflow:
- Submit message (source chain).
- Relay the message via Timechain shards.
- Execute the message (destination chain).
- Workflow:
Note
Analog GMP enhances Circle CCTP by automating USDC transfers, eliminating the need for end-user redemptions and gas payments on destination chains. It also provides tools for troubleshooting failed transactions, improving both UX and security. For more details, check out the Analog GMP docs.
Architectural Components
The Zenswap protocol comprises various components spread across both on-chain and off-chain systems, as illustrated in the figure below:
See below for a detailed overview of their operation:
- Actor (User): Initiates the cross-chain swap request.
- Router Contracts: Main contract handling the routing of swaps on source and destination blockchains. Interfaces with Circle’s CCTP contract for burning and minting USDC.
- Analog Gateway Smart Contracts (GSCs): Facilitates cross-chain operations by receiving and processing swap requests from the Router Contract.
- Chronicles Shards: These are off-chain entities that listen for gateway events, validate TSS, and relay events to the Timechain.
- Task Queue–Timechain: Part of the Timechain, responsible for event handling and task management.
- Circle (CCTP Contract): Manages the burning and minting of USDC tokens during cross-chain swaps.
- Global Router–Off-chain: Calculates potential swap routes off-chain for scalability.
- Timechain: Maintains a record of transactions and events within the ledger.
Core Components
- ZenSwap: Core contract for local swaps and initiating cross-chain transactions.
- ZenSwapGmpPlugin: Handles cross-chain USDC bridging via CCTP and Analog GMP.
- UniswapWrapper: Abstract contract for Uniswap Universal Router interactions.
- CCTP (Circle): Facilitates cross-chain USDC transfers with burn/mint mechanics.
- GMP Gateway: Analog’s general message passing layer for cross-chain communication.
Transaction Lifecycle
Here's a detailed breakdown of the transaction lifecycle (Classic Mode):
- User Initiates Swap (Source Chain)
- Calls ZenSwap.swapSend() with swap parameters for source/destination chains.
- Tokens are swapped locally to USDC via a supported DEX, e.g., Uniswap.
- Bridging Initiation
- USDC is sent to ZenSwapGmpPlugin.
- Plugin burns USDC via CCTP and sends a GMP message containing:
- CCTP burn proof
- Destination swap parameters
- Recipient address
- Cross-Chain Messaging
- Analog GMP relays message to destination chain.
- Destination Chain Execution
- ZenSwapGmpPlugin.onGmpReceived() processes message:
- Mints USDC via CCTP
- Triggers ZenSwap.onReceive()
- Final swap from USDC to target token occurs via supported DEX, e.g., Uniswap.
- ZenSwapGmpPlugin.onGmpReceived() processes message:
- Funds Delivery
- Swapped tokens sent to recipient. If swap fails, USDC goes to fallback address.
Note on Boost Mode-Only Flow
If a plugin using only Boost Mode (without GMP) is used, the transaction undergoes the following steps:
Source Chain (Initiation):
// ZenSwap Contract function swapSend() { // 1. Swap input token -> USDC via Uniswap // 2. CCTPv2Plugin.depositForBurn(USDC) // 3. Burn USDC + generate CCTP message }Note that CCTPv2Plugin emits an event containing the CCTP message details, but does not call the GMP Gateway.
Cross-Chain Transfer:
// ZenSwapCCTPv2.sol function _cctpSend() { // 1. Wait for Circle attestation // 2. Transmit raw CCTP message // 3. Emit MessageSent event }Destination Chain (Completion):
// ZenSwapCCTPv2.sol function receiveMessage() { // 1. Verify CCTP attestation // 2. Mint USDC via message validation // 3. Execute final swap via ZenSwap.onReceive() }
Core Functionalities
ZenSwap Contract
Responsibilities:
- Execute local token swaps using supported DEX.
- Coordinate with plugins for cross-chain operations.
- Handle incoming cross-chain transactions.
Key Functions:
function swapSend(...)// Initiate cross-chain swapfunction onReceive(...)// Handle incoming cross-chain transfers
ZenSwapGmpPlugin Contract
Responsibilities:
- Manage CCTP token burning/minting
- Handle GMP message passing
- Implement fee structure
- Provide fallback mechanisms
Key Functions:
function submit(...)// Initiate cross-chain transferfunction onGmpReceived(...)// Process incoming messages
UniswapWrapper
Responsibilities:
- Interface with Uniswap Universal Router
- Handle token approvals via Permit2
- Execute swap operations
Fee Structure
ZenSwap's fee structure is designed to cover operational costs while providing transparent pricing for cross-chain token swaps.
Protocol Fee: ZenSwap charges a fixed protocol fee on cross-chain transactions:
- The fee is deducted from the USDC amount being bridged between chains.
- This fee accumulates in the ZenSwapGmpPlugin contract, is set by the protocol admin, and can be adjusted over time.
- Transactions require the bridging amount to exceed the fee (amount > fee), otherwise, the transaction will revert with
ErrorNotEnoughForFeeerror.
Analog GMP Fee: Users will also need to pay for the Analog GMP costs:
- These fees are paid in the source chain's native token (e.g., ETH on Ethereum) and vary based on:
- Destination network
- Message size
- Gas limit specified for execution on the destination chain
- Users can estimate these costs before transaction submission using the estimateMessageCost function.
Swap Fees: Beyond the protocol-specific fees, users will also incur standard swap fees on the supported DEXs:
- Uniswap Fees: When performing token swaps through the Universal Router, standard Uniswap liquidity provider fees apply (typically 0.05%-1.00% depending on the pool).
- Slippage Protection: While not a fee per se, users should account for potential slippage in their transactions, especially for volatile or low-liquidity pairs.
Gas Fees: Network transaction costs on both chains.
Scenario 1: Single-Chain Swap Let's consider a user swapping 1,000 USDC for ETH on Ethereum
- Transaction Details:
- Source token: 1,000 USDC
- Destination token: ETH
- Chain: Ethereum
- Fee Breakdown:
- Uniswap LP fee: 0.3% (3 USDC)
- Gas fees: ~$5 worth of ETH for contract interaction
- Net Result:
- The user receives approximately 997 USDC worth of ETH (minus gas fees), with the 0.3% fee going to Uniswap LPs.
Scenario 2: Cross-Chain Swap Now, let's analyze a cross-chain swap from Ethereum (ETH) to Polygon (MATIC):
- Transaction Details:
- Source chain: Ethereum
- Source token: 1,000 USDC
- Destination chain: Polygon
- Destination token: MATIC
- Fee Breakdown:
- Initial swap fee: 0.3% for swapping source token to USDC.
- Protocol fee: 5 USDC fixed fee deducted from bridged amount.
- Analog GMP fee: 0.01 ETH (~$25) paid in ETH on source chain.
- Destination swap fee: 0.3% of remaining amount (995 USDC) for swapping USDC to MATIC on Polygon
- Gas fees: Ethereum transaction (~$10-15 in ETH)
- Net Result:
- The recipient on Polygon receives approximately 992 USDC worth of MATIC (995 minus 0.3% destination swap fee). Total cost to user includes 5 USDC protocol fee, 0.01 ETH messaging fee, plus gas fees.
Developers
Transaction Status Tracking
As your swap progresses, you'll see these status updates (visible via API/SDK or Explorer):
- Initial: Transaction submitted
- SourceSwap: Token A successfully swapped to USDC
- USDCBurn: USDC burned on the source chain
- MintPending: Awaiting USDC mint on destination chain
- USDCReceived: USDC received on the destination chain
- DestinationSwap: USDC swapped to Token B
- Completed: Transaction fully completed
If errors occur, you'll see:
- SourceError: Error on source chain (with reason)
- DestinationError: Error on destination chain (with reason)
Failsafe Mechanisms
Zenswap implements robust error handling to protect your assets:
- Source Chain Errors:
- If Token A to USDC swap fails, the transaction reverts completely.
- If CCTP burn fails, the transaction reverts.
- Destination Chain Errors:
- If CCTP mint fails, the system attempts resolution based on the error type (may involve manual intervention or automated retries).
- If USDC to Token B swap fails, you can withdraw your USDC directly from the contract on the destination chain.
All transaction states are logged for transparency and troubleshooting.
Zenswap SDK
The Zenswap SDK is a comprehensive toolkit that allows you to integrate cross-chain token swapping and transfers into your dApps.
Features
- Cross-Chain Swaps & Transfers: Swap tokens and transfer them across chains in a single operation.
- Automatic Route Finding: Finds the best swap and bridge routes for your transaction.
- Fee Estimation: Calculates gas, cross-chain, and protocol fees.
- Provider Abstraction: Works with multiple RPC providers and wallets.
- Local Storage Utilities: For caching and persistence.
- Math Utilities: For precise, high-precision calculations.
For more details about installation and instantiation, see SDK Quickstart.
Getting Started: SwapRouter
The SwapRouter class is the primary interface for interacting with the Zenswap protocol via the SDK. It abstracts away the complexities of contract interactions and route finding.
import {
SwapRouter,
NetworkId,
ChainId,
getNetworkId,
getChainId,
} from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
// The SDK comes with default configurations for testnet deployments (Sepolia and Arbitrum Sepolia),
// GMP IDs, fee parameters, network configurations, and token details.
// Create a router instance with default configurations
const router = new SwapRouter();
// Alternatively, you can override specific configurations
const customContracts = {
[ChainId.EthereumMainnet]: {
zenswap: "0x...", // Your deployed Zenswap contract address
gmpPlugin: "0x...", // Your deployed GMP plugin address
gmpGateway: "0x...", // Your deployed GMP gateway address
},
};
const customGmpIds = {
[ChainId.EthereumMainnet]: 1,
};
const customFeePercent = 0.3; // 0.3% protocol fee
const customFeeRecipient = "0x..."; // Address to receive protocol fees
// Create a router instance with custom configurations
const customRouter = new SwapRouter(
customContracts, // Pass null to use defaults
customGmpIds, // Pass null to use defaults
customFeePercent, // Pass null to use defaults
customFeeRecipient // Pass null to use defaults
);
The Zenswap SDK provides the following strategies to accommodate diverse use cases:
- Swap: Same-chain swap (e.g., ETH -> USDC on Ethereum).
- SwapAndTransfer: Swap on source chain, bridge intermediate token (USDC), transfer to destination (e.g., ETH on Sepolia -> USDC on Arbitrum Sepolia).
- TransferAndSwap: Bridge intermediate token (USDC), swap on destination chain (e.g., USDC on Sepolia -> ARB on Arbitrum Sepolia).
- Transfer: Direct bridge of a token (typically USDC) between chains.
- SwapAndSwap: Swap on source (e.g., ETH -> USDC), bridge USDC, swap on destination (USDC -> ARB).
- Wrap / Unwrap: Convert between native ETH and WETH on the same chain.
Basic Usage Examples
1. Finding a Swap Route
The findRoute method identifies the optimal strategy and parameters for a given swap or transfer.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken, ChainId } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
import { ethers } from "ethers"; // Example, ensure ethers is installed if you use it
// Assuming you have initialized a router and have NetworkToken objects
const tokenIn = {
address: "0x...", // Address of the input token contract
chainId: ChainId.EthereumSepolia, // Chain ID of the input token
decimals: 18, // Decimals of the input token
symbol: "TOKEN_IN",
name: "Input Token",
};
const tokenOut = {
address: "0x...", // Address of the output token contract
chainId: ChainId.ArbitrumSepolia, // Chain ID of the output token
decimals: 6, // Decimals of the output token (e.g., USDC)
symbol: "USDC",
name: "USD Coin",
};
// Define input parameters for the swap/transfer
const swapParams = {
input: tokenIn, // NetworkToken object for input token
output: tokenOut, // NetworkToken object for output token
amount: "1.5", // Amount to swap as a string (for precision)
recipient: "0x...", // The final recipient address on the destination chain
slippagePercent: 0.5, // Slippage tolerance in percentage (e.g., 0.5 for 0.5%)
deadlineInSeconds: 1800, // Transaction deadline in seconds (e.g., 1800 for 30 minutes)
};
// Find the best route
const route = await router.findRoute(swapParams);
if (route) {
console.log("Swap route found:");
console.log("Input amount:", route.input.amount);
console.log("Output amount:", route.output.amount);
console.log("Price impact:", route.priceImpact, "%");
console.log("Strategy:", route.strategy);
// The route.method contains the transaction parameters ready for execution
const txParams = route.method?.parameters;
// Execute the transaction using your preferred web3 provider (e.g., ethers.js)
// Ensure the signer has enough native token for gas and approved the input token if required
// const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
// const signer = await provider.getSigner();
// const tx = await signer.sendTransaction(txParams);
// await tx.wait(); // Wait for the transaction to be mined
} else {
console.log("No route found for the given parameters.");
}
2. Cross-chain Token Transfer
The findRoute method can also determine the best route for a direct cross-chain token transfer.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken, ChainId } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
// Assuming you have initialized a router and have NetworkToken objects for USDC on different chains
const usdcEthereum = {
address: "0x...", // USDC address on Ethereum
chainId: ChainId.EthereumSepolia,
decimals: 6,
symbol: "USDC",
name: "USD Coin",
};
const usdcPolygon = {
address: "0x...", // USDC address on Polygon
chainId: ChainId.PolygonMumbai, // Assuming PolygonMumbai from doc, adjust if needed
decimals: 6,
symbol: "USDC",
name: "USD Coin",
};
// Example of a cross-chain transfer from Ethereum Sepolia to Polygon Mumbai
const transferParams = {
input: usdcEthereum, // USDC on Ethereum Sepolia
output: usdcPolygon, // USDC on Polygon Mumbai
amount: "100", // Amount to transfer as a string
recipient: "0x...", // Recipient address on Polygon Mumbai
slippagePercent: 0.1, // Slippage tolerance (can be set to 0 for direct transfers)
deadlineInSeconds: 1800,
};
const transferRoute = await router.findRoute(transferParams);
if (transferRoute) {
console.log("Transfer route found:", transferRoute.strategy);
console.log("Input amount:", transferRoute.input.amount);
console.log("Output amount:", transferRoute.output.amount);
// The transferRoute.method contains the transaction parameters
const txParams = transferRoute.method?.parameters;
// The transferRoute.fee contains the estimated network gas fee on the source chain
console.log(
"Estimated source chain gas fee:",
transferRoute.fee.amount,
transferRoute.fee.token.symbol
);
// The transferRoute.transferFee contains the estimated gas fee on the destination chain for claiming/processing
if (transferRoute.transferFee) {
console.log(
"Estimated destination chain transfer fee:",
transferRoute.transferFee.amount,
transferRoute.transferFee.token.symbol
);
}
// The transferRoute.gmpFee contains the estimated fee for the cross-chain message passing
if (transferRoute.gmpFee) {
console.log(
"Estimated GMP fee:",
transferRoute.gmpFee.amount,
transferRoute.gmpFee.token.symbol
);
}
// Execute the transaction using your web3 provider
// const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
// const signer = await provider.getSigner();
// const tx = await signer.sendTransaction(txParams);
// await tx.wait();
} else {
console.log("No transfer route found.");
}
3. Getting a Quote Without Executing
If you only need an estimated output amount and fees without preparing a full transaction.
// const quote = await router.quote(swapParams); // Uses same params as findRoute
// if (quote) {
// console.log("Estimated output:", quote.output.amount, quote.output.token.symbol);
// console.log("Estimated Network Fee:", quote.fee.amount, quote.fee.token.symbol);
// // ... log transferFee, gmpFee if applicable
// }
4. Cross-Chain Fees
Your cross-chain operations include these fees:
- Swap Fees (Uniswap pool fees)
- Bridge Fees:
- CCTP message fees
- GMP costs
- Protocol Fees (configurable)
For more details, see Fee Structure. The SDK helps manage these fees:
- findRoute() and quote(): Return estimates for network, transfer, and GMP fees.
- prepareGmpFee(): Fetch the estimated GMP fee before starting a cross-chain transaction.
- createDirectRoute(): Set a custom GMP fee to deduct from the transfer amount before calculating the final output on the destination chain.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken, ChainId, RouteType } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk"; // Added RouteType
// Assuming you have initialized a router and have a NetworkToken object for the token being bridged
const proxyToken = {
address: "0x...", // Address of the token to bridge
chainId: ChainId.EthereumSepolia, // Chain ID of the token
decimals: 18,
symbol: "PROXY",
name: "Proxy Token",
};
// Calculate the estimated GMP fee for a cross-chain message involving this token
// const gmpFee = await router.prepareGmpFee(proxyToken);
// console.log("Estimated GMP fee:", gmpFee.amount, gmpFee.token.symbol);
// When creating a direct transfer route, the GMP fee is deducted from the input amount
// const amountToTransfer = BigInt(100e18); // Example amount as BigInt
// const transferRoute = router.createDirectRoute(
// amountToTransfer, // Total amount on the source chain
// proxyToken, // Source token
// // Assuming the destination token is the same token on a different chain
// { ...proxyToken, chainId: ChainId.PolygonMumbai }, // Corrected to PolygonMumbai
// RouteType.Transfer,
// BigInt(gmpFee.amount) // GMP fee amount to deduct
// );
// console.log("Input amount:", amountToTransfer);
// console.log("GMP fee deducted:", gmpFee.amount);
// console.log(
// "Output amount on destination chain (before any destination fees):",
// transferRoute.output.amount,
// transferRoute.output.token.symbol
// );
Note that the fee retained by the ZenSwapGmpPlugin on the destination chain is handled within the plugin's submit and onGmpReceived functions and is not directly deducted via createDirectRoute. The SDK's fee estimations for the transfer fee component (distinct from the GMP fee) would account for this destination-side fee.
5. Boost Mode Integration (for CCTP V2 routes)
The Zenswap SDK offers a “Boost Mode” feature for swaps across chains using CCTP V2 routes. You can activate Boost Mode by including a boostParams object when calling the findRoute method.
The boostParams object accepts the following parameters:
maxFeePercent: Maximum fee percentage (converted to absolute value by SDK). Sets the maximum destination chain fee as a percentage of swap amount.rewardAmount: Relayer incentive in USDC. Specify reward amount (in smallest USDC units) to incentivize faster transaction processing.minFinalityThreshold. Block confirmations required. Minimum source chain confirmations before message finalization (lower = faster, higher = safer).
Usage Example
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
// Define input token (example)
// const tokenIn = new NetworkToken({ chainId: 1, address: "0x...", decimals: 18, symbol: "SRC" });
// Define output token (example)
// const tokenOut = new NetworkToken({ chainId: 10, address: "0x...", decimals: 18, symbol: "DST" });
// Define input parameters
const swapParams = {
input: tokenIn, // NetworkToken object for input token
output: tokenOut, // NetworkToken object for output token
amount: "1.5", // Amount to swap as string
recipient: "0xRecipientAddressOnDestinationChain", // Recipient address
slippagePercent: 0.5, // Slippage tolerance (0.5%)
deadlineInSeconds: 1800, // Transaction deadline (30 minutes)
};
// Define boost parameters
const boostParams = {
maxFeePercent: 0.01, // Example: Willing to pay up to 0.01% of swap amount as CCTP max fee
rewardAmount: "1000000", // Example: 1 USDC (since USDC usually has 6 decimals, adjust based on SDK expectation or if it means units of the token)
// The ZenSwapCCTPv2.sol contract PluginParams.rewardAmount is a uint256.
// If it's in USDC units, it would be 1 * 10^6 for 1 USDC.
minFinalityThreshold: 10, // Example: Wait for 10 confirmations on source chain
};
// Find the best route with boost mode
// This assumes the SDK internally maps these boostParams to the
// `pluginParams` structure required by ZenSwap.sol for the CCTP plugin.
async function findBoostedRoute() {
const router = new SwapRouter(); // Initialize router
try {
const route = await router.findRoute(swapParams, boostParams);
if (route) {
console.log("Boost mode route found:");
console.log("Input amount:", route.input.amount.toString());
console.log("Output amount:", route.output.amount.toString());
console.log("Price impact:", route.priceImpact, "%");
console.log("Strategy:", route.strategy);
// The route.method contains the transaction parameters
const txParams = route.method?.parameters;
console.log("Transaction parameters for boosted swap:", txParams);
// Execute the transaction using your preferred web3 provider
// e.g., with ethers.js:
// const signer = yourEthersSigner;
// const tx = await signer.sendTransaction(txParams);
// console.log("Transaction sent:", tx.hash);
// await tx.wait();
// console.log("Transaction confirmed!");
} else {
console.log("No suitable boost mode route found.");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error finding boosted route:", error);
}
}
// findBoostedRoute(); // Call the async function
Advanced Features
1. Fee Calculation and Gas Estimation
The SDK provides utilities for advanced fee management:
import { SwapRouter, NetworkId, SwapFee, getMaxValue, isNativeToken, ChainId } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk"; // Added ChainId
import { ethers } from "ethers";
// 1. Estimate gas for a specific transaction (requires a provider)
// const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider("YOUR_RPC_URL");
// const networkId = NetworkId.EthereumSepolia;
// const txRequest = {
// to: "0x...", // Transaction recipient
// data: "0x...", // Transaction calldata
// value: BigInt(0), // Transaction value in native token
// from: "0x...", // Transaction sender
// };
// const gasUsed = await SwapRouter.estimateGasUsed(provider, networkId, txRequest);
// console.log("Estimated gas used:", gasUsed);
// 2. Create a SwapFee instance with custom coefficients for gas price calculation
// const networkFee = {
// token: { address: "0x...", chainId: ChainId.EthereumSepolia, decimals: 18, symbol: "ETH", name: "Ether" },
// gasLimit: BigInt(21000), // Example gas limit
// baseFeePerGas: BigInt(100e9), // Example base fee (100 Gwei)
// };
// const swapFee = new SwapFee(
// networkFee.token,
// networkFee.gasLimit,
// networkFee.baseFeePerGas
// );
// swapFee.baseCoeff = 1.2; // Adjust base fee multiplier (e.g., for faster confirmation)
// swapFee.priorityCoeff = 1.5; // Adjust priority fee multiplier
// swapFee.additionalValue = BigInt(ethers.parseEther("0.01")); // Add additional value for gas
// console.log("Estimated total fee with coefficients:", swapFee.amount);
// 3. Get the maximum available amount considering balance and fees
// const balance = BigInt(ethers.parseEther("1")); // User's balance
// const combinedFeeAmount = BigInt(ethers.parseEther("0.02")); // Total estimated fees
// const isInputNativeToken = true; // True if the input token is the native currency
// const maxAmount = getMaxValue(balance, combinedFeeAmount, isInputNativeToken);
// console.log("Maximum tradable amount:", maxAmount);
2. Transaction Lifecycle Management
The SDK manages the lifecycle of cross-chain transactions.
import {
SwapRouter,
TxState,
generateTxId,
waitForEvmTransactionMined,
waitForDestinationTx, // Helper (may need implementation based on plugin)
} from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
// Assuming you have a route and a signer
// const route = await router.findRoute(swapParams);
// const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
// const signer = await provider.getSigner();
// if (route && route.method) {
// const { data, value, to } = route.method.parameters;
// const txRequest = {
// to: to,
// data: data,
// value: value.toString(), // Ensure value is a string
// // Add gas price/limit parameters as needed
// };
// // Create initial transaction details object
// const txDetails = {
// id: generateTxId(), // Generate a unique ID for tracking
// input: route.input,
// output: route.output,
// networkFee: route.fee,
// transferFee: route.transferFee,
// gmpFee: route.gmpFee,
// routerFee: route.routerFee,
// priceImpact: route.priceImpact,
// estimatedTime: route.estimatedTime,
// startTime: Date.now(),
// state: TxState.Pending, // Initial state
// sourceHash: undefined,
// destHash: undefined,
// received: undefined,
// };
// console.log("Transaction initiated:", txDetails.id);
// try {
// // Execute the transaction on the source chain
// const tx = await signer.sendTransaction(txRequest);
// txDetails.sourceHash = tx.hash;
// txDetails.state = TxState.Confirming;
// console.log("Source transaction sent:", tx.hash);
// // Wait for the source transaction to be mined
// await waitForEvmTransactionMined(tx);
// console.log("Source transaction mined.");
// // For cross-chain transactions, monitor for completion on the destination chain
// if (txDetails.transferFee) {
// txDetails.state = TxState.Executing;
// console.log("Monitoring for destination transaction...");
// // You would need a mechanism to monitor for the corresponding transaction
// // on the destination chain, possibly by listening for events emitted
// // by the destination receiver contract (e.g., the 'Received' event in ZenSwap).
// // The `waitForDestinationTx` function is a placeholder for this logic.
// // It would typically involve polling or subscribing to destination chain events
// // using the source transaction hash or other identifiers embedded in the cross-chain message.
// // Example placeholder for waiting (needs actual implementation based on monitoring setup)
// // const destTxResult = await waitForDestinationTx(tx.hash, route.output.token.chainId);
// // if (destTxResult) {
// // txDetails.destHash = destTxResult.hash;
// // txDetails.received = {
// // token: route.output.token,
// // amount: destTxResult.amount, // Amount received on destination
// // };
// txDetails.state = TxState.Done;
// console.log("Destination transaction completed.");
// // } else {
// // txDetails.state = TxState.Failed;
// // console.error("Destination transaction failed or timed out.");
// // }
// } else {
// // For same-chain swaps
// txDetails.state = TxState.Done;
// console.log("Swap completed on source chain.");
// }
// txDetails.endTime = Date.now();
// txDetails.executionTime = txDetails.endTime - txDetails.startTime;
// console.log("Transaction finished. State:", txDetails.state);
// } catch (error) {
// console.error("Transaction failed:", error);
// txDetails.state = TxState.Failed;
// txDetails.endTime = Date.now();
// txDetails.executionTime = txDetails.endTime - txDetails.startTime;
// }
// // Update UI or application state with the final txDetails
// }
- Transaction States: The SDK defines states to track the progress of a transaction:
- Pending: Transaction created, not yet sent.
- Confirming: Transaction sent to the network, waiting to be mined.
- Executing: Source transaction confirmed, cross-chain operation in progress.
- Done: Transaction completed successfully on all relevant chains.
- Failed: Transaction encountered an error at some stage.
- Transaction Details: A TxDetails object provides comprehensive information about a transaction:
- Input and output token details and amounts.
- Breakdown of network, transfer, GMP, and router fees.
- Estimated price impact and completion time.
- Start and end times, and total execution time.
- Transaction hashes on both source and destination chains (for cross-chain).
- Amount of tokens received on the destination chain.
- Progress Monitoring: Applications can monitor TxDetails to provide users with real-time feedback on the transaction status.
- For cross-chain swaps, this involves tracking confirmation on the source chain and execution on the destination chain. The specific implementation for monitoring destination chain execution will depend on how the cross-chain plugin signals completion, such as by emitting an event that can be tracked.
3. Token Approvals
For ERC-20 tokens (which are not the native currency), the Zenswap contract (or the Permit2 contract it uses) needs permission to spend the user's tokens. The SDK helps manage these approvals.
import { SwapRouter, NetworkToken, ChainId, approveToken, waitForEvmTransactionMined } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk"; // Added waitForEvmTransactionMined
import { BigNumber } from "ethers"; // Using BigNumber for comparisons
import { ethers } from "ethers";
// Assuming you have a signer, the input token details, the required amount, and the spender address (ZenSwap contract address)
// const signer = await new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum).getSigner();
// const inputToken = { address: "0x...", chainId: ChainId.EthereumSepolia, decimals: 18, symbol: "TOKEN", name: "My Token" };
// const amountIn = BigInt(ethers.parseUnits("100", inputToken.decimals)); // Amount as BigInt
// const zenswapContractAddress = "0x..."; // Address of the ZenSwap contract
// Check the current allowance
// const inputTokenContract = new ethers.Contract(inputToken.address, ["function allowance(address owner, address spender) view returns (uint256)"], signer);
// const allowance = await inputTokenContract.allowance(await signer.getAddress(), zenswapContractAddress);
// Check if approval is needed (allowance is less than the amount to spend)
// const isApproved = BigNumber.from(allowance.toString()).gte(BigNumber.from(amountIn.toString()));
// If approval is needed, execute the approval transaction
// if (!isApproved) {
// console.log("Approval required. Sending approval transaction...");
// const approvalTx = await approveToken(
// signer,
// inputToken.address,
// zenswapContractAddress,
// amountIn // Approve the specific amount needed
// // Or use ethers.MaxUint256 for unlimited approval
// );
// await waitForEvmTransactionMined(approvalTx); // Wait for the approval to be confirmed
// console.log("Token approved.");
// } else {
// console.log("Token already approved.");
// }
Note
The ZenSwap contract utilizes Permit2 (UniswapWrapper), which requires a slightly different approval flow involving the Permit2 contract itself. The SDK's findRoute method and transaction execution logic should handle the necessary Permit2 interactions internally, requiring the user to approve the Permit2 contract to spend their tokens.
4. Periodic Quote Updates
In dynamic market conditions, it is crucial to provide users with up-to-date price quotes. The SDK facilitates periodic quote updates.
import { SwapRouter } from "@zenswap-analog/sdk";
// const QUOTE_UPDATE_INTERVAL = 15000; // 15 seconds
// const QUOTE_DEBOUNCE_TIMEOUT = 1000; // 1 second
// Assuming you have a function to update your UI with a new quote result
// function setQuoteResult(result: any) { /* ... */ }
// Assuming you have a way to track the current quote request ID to avoid race conditions
// let currentQuoteId: number | undefined;
// function isCurrentQuoteId(id: number): boolean { return currentQuoteId === id; }
// function generateQuoteId(): number { return Date.now(); }
// Create a debounced quote function to avoid excessive calls
// const debouncedQuote = debouncedHandler(updateQuote, QUOTE_DEBOUNCE_TIMEOUT); // debouncedHandler needs to be defined or imported
// Schedule the next quote update
// function scheduleQuoteUpdate(quoteId: number) {
// setTimeout(() => {
// if (isCurrentQuoteId(quoteId)) {
// updateQuote(quoteId);
// }
// }, QUOTE_UPDATE_INTERVAL);
// }
// Function to update the quote
// async function updateQuote(quoteId: number) {
// try {
// const result = await router.findRoute(swapParams); // Use the latest swapParams
// if (result && isCurrentQuoteId(quoteId)) {
// // await updateGasEstimates(result); // Optionally update gas estimates
// setQuoteResult(result);
// scheduleQuoteUpdate(quoteId); // Schedule the next update
// }
// } catch (error) {
// console.error("Quote update failed:", error);
// // Handle the error (e.g., display an error message, stop updates)
// }
// }
// To start periodic updates:
// const initialQuoteId = generateQuoteId();
// currentQuoteId = initialQuoteId;
// updateQuote(initialQuoteId); // Get the initial quote
// To stop periodic updates (e.g., when the user navigates away):
// currentQuoteId = undefined; // Invalidate the current quote ID
This pattern ensures that quote updates are managed efficiently, preventing rapid-fire requests and handling potential delays or errors.
Tokenomics
Stakeholders
There are three key roles in the Zenswap protocol:
- Liquidity providers (LPs), who add USDC to the liquidity pools for the supported assets and may also provide short-term loans that power the Boost Mode. For more details, see Boost Mode. In return, LPs earn fees and rewards.
- Swappers, who use the liquidity in the pools to swap assets on an ad-hoc basis. They pay fees in the process.
- Market makers (MMs), who contribute to liquidity pools by monitoring and rebalancing them. They incur fees but anticipate profits in return for their services.
Token Overview
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Ticker | ZSWAP |
| Total supply (at genesis) | 1,000,000,000 |
| Decimals | 18 |
| Base unit | ZEP |
| Conversion | 1 ZEP = 10-18 ZSWAP |
Token Allocation
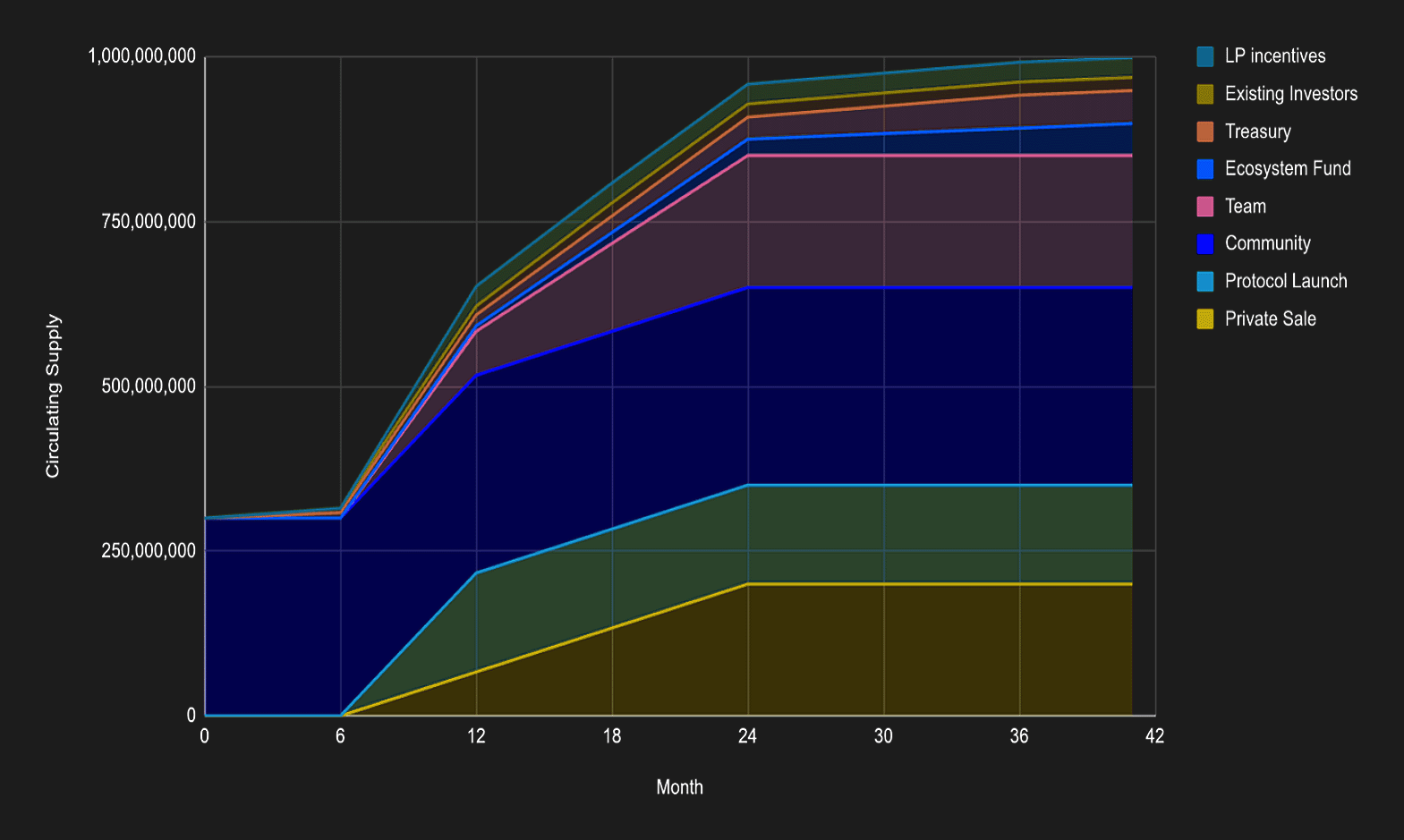
At its launch, Zenswap will have a total supply of 1,000,000,000 ZSWAP, allocated across 8 categories, as outlined in the table below:
| Category | Description | % |
|---|---|---|
| Private Sale | A pool allocated for Zenswap’s early and later stage private round investors. | 20 |
| Protocol Launch | A pool allocated towards bootstrapping USDC liquidity during launch on external chains using token auction. | 14 |
| Community | A pool for community incentives, including airdrops and marketing, to support Zenswap's long-term success. | 30 |
| Team | A pool allocated to core team members of Zenswap, including advisors and developers. | 20 |
| Ecosystem Fund | A pool allocated towards DEXs and relayers integration. Also, it will incentivize dApps to integrate with Zenswap. | 5 |
| Treasury | A pool allocated to cater for the future protocol development and bounties. It also will act as an emergency fund for users. | 5 |
| Existing Investors | A pool allocated for existing investors. | 3 |
| LP Incentives | A pool allocated to cater to initial emissions for liquidity provider incentives. | 3 |
Unlock Schedule
The 1 billion ZSWAP minted at Genesis will be distributed over time as per the unlock schedule shown below:
FAQ
How long does the cross-chain swap take?
The duration of a cross-chain swap largely depends on the finality time of the origin chain. Analog GMP and Circle CCTP prioritize security by delaying the minting process on the destination chain until the burning process on the source chain is definitively confirmed, thus mitigating the risk of chain reorgs. Boost Mode significantly reduces this time by providing instant liquidity on the destination chain.
Is it possible to cancel a transaction once it is initiated?
No. You cannot reverse a transaction once it is initiated and confirmed on a blockchain. We recommend carefully reviewing the transaction details before submitting it to avoid errors.
What wallets does Zenswap support?
Zenswap supports major Substrate and EVM wallets like MetaMask, SubWallet, Fearless Wallet, Talisman and Enkrypt. See Wallet Support for details.
Can I swap my funds between different wallets?
Yes, Zenswap lets you easily swap assets across various networks and wallets. After connecting your wallet, swaps within the same wallet across different networks (e.g., Ethereum to Polygon) only require network selection. However, for swaps between different wallets on different networks (e.g., Metamask on Ethereum and WalletConnect on Astar), you’ll need to manually enter the destination wallet address in the recipient field.
How does Zenswap ensure there is no slippage for transactions involving huge amounts?
Zenswap leverages Circle CCTP to ensure boundless liquidity for the USDC transfer portion. This eliminates slippage concerns for the cross-chain USDC movement. Slippage may still occur during the initial swap (Token A -> USDC on source) and final swap (USDC -> Token B on destination) depending on the liquidity available in the underlying DEX pools used for those swaps. Zenswap aims to minimize this by integrating with deep liquidity sources.
Where can I monitor the status of my cross-chain swap?
To check the status of your cross-chain swap, visit the Zenswap Explorer for real-time updates. You can also check your transaction on the Timechain Explorer by searching for your transaction hash.
What is Timechain Explorer?
The Timechain Explorer allows you to monitor the progress of your Analog GMP transactions, including Zenswap transfers. To check the status of a specific transaction, input its hash or ID into the Timechain Explorer’s search bar and press Enter.
Do I need to keep my browser open during the entire transfer process?
No. Your Zenswap transfer will progress even if you close your browser. You can track the swap’s status at any time using the Timechain Explorer or Zenswap Explorer.
What is a Boost Mode?
Boost Mode is Zenswap’s high-speed feature that enables quick cross-chain swaps. It leverages Liquidity Providers (LPs) to offer short-term loans, ensuring swift transaction completion on the destination chain almost instantly after your source transaction confirms. See Boost Mode for more details.
How do I know if my swap is completed?
You can verify your transfer’s completion in two ways: by checking the Zenswap Explorer or by verifying your account balance on the destination blockchain. To track the progress of your swap, you can either use the Zenswap Explorer or search for the transaction’s hash or ID in the Timechain Explorer.
How can I add my asset to Zenswap?
For a cross-chain swap to be facilitated, chains and assets must first be supported by Analog GMP and Circle CCTP (for USDC routing). The initial asset support relies on the tokens available on integrated DEXs like Uniswap on the supported chains. See “Supported Blockchains & Assets” for the current list. Adding new assets primarily depends on their availability on supported DEXs within the supported chains.